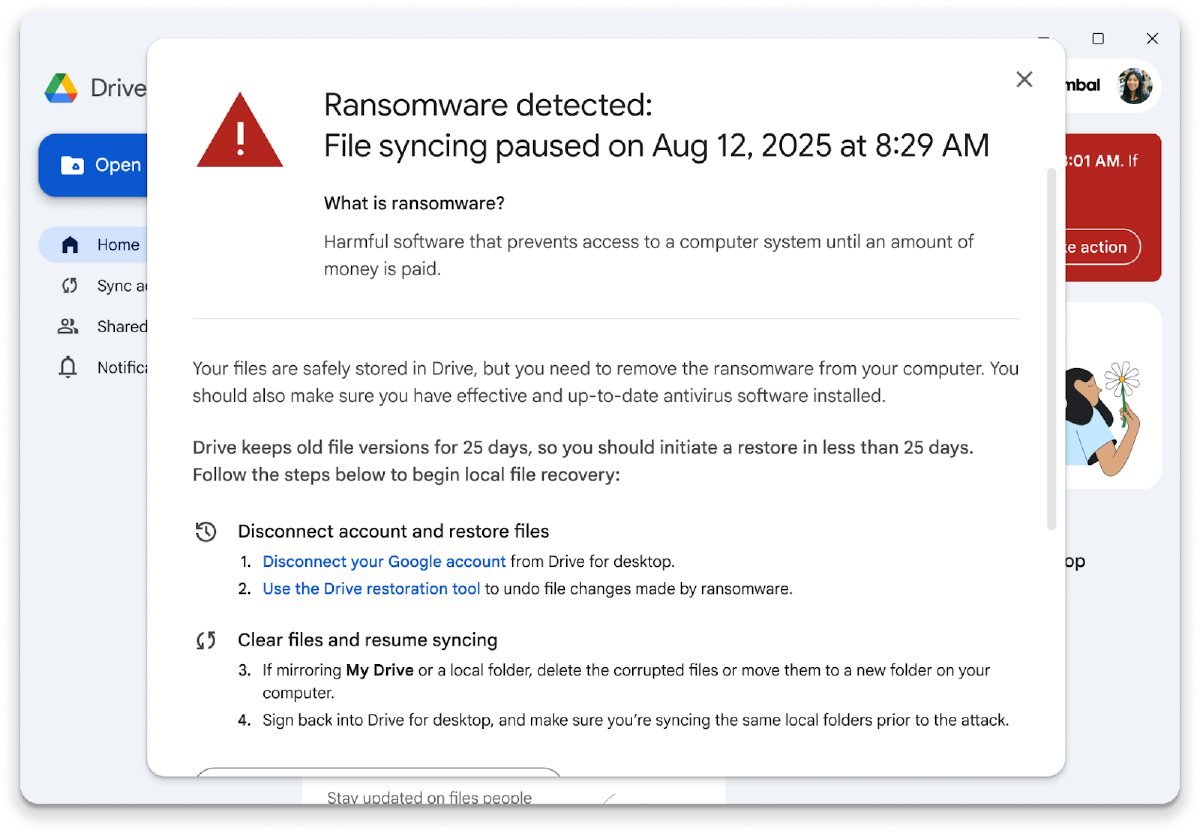
Google just launched AI-powered ransomware detection in Drive for desktop. When ransomware tries to encrypt your files, Drive automatically stops syncing and lets you restore everything with a few clicks.
This isn’t about preventing ransomware from getting in. It’s about stopping it from being effective once it’s already on your system.
How it works#
AI detection: A specialized model, trained on millions of ransomware samples, watches for signs that files are being maliciously modified or encrypted en masse.
Automatic intervention: When Drive detects suspicious activity, it immediately pauses file syncing to prevent encrypted files from spreading to the cloud.
Easy restoration: Users get desktop and email alerts with a simple web interface to restore multiple files to their previous, healthy state.
Admin visibility: IT teams receive alerts in the Admin console and can review detailed audit logs of ransomware activity.
The key insight: instead of trying to stop ransomware from executing, Google is stopping it from achieving its goal of corrupting your important files.
Why this approach matters#
Traditional antivirus focuses on detecting malicious code before it runs. That’s important, but ransomware attacks keep succeeding despite AV protection.
Google’s bet: Ransomware has to encrypt files to be effective. If you can detect that mass encryption and intervene quickly, you can neutralize the attack even if the malware got through.
The signature: Ransomware’s core behavior is attempting to encrypt or corrupt files en masse. That’s detectable, regardless of how the specific malware variant works.
Speed matters: The faster you can stop the encryption and restore files, the less damage occurs. Drive’s integration makes this nearly instant.
What’s protected (and what isn’t)#
Protected:
- Files synced through Drive for desktop on Windows and macOS
- PDF files, Microsoft Office documents, and other non-Google formats
- Files that get encrypted by ransomware running on your local machine
Already safe:
- Native Google Workspace documents (Docs, Sheets, Slides) aren’t affected by ransomware
- ChromeOS has never had a successful ransomware attack
The gap: This protects against ransomware on traditional operating systems affecting files that sync to Drive. It doesn’t protect local-only files or prevent the initial infection.
The technical reality#
What Google built: An AI model that continuously analyzes file changes, looking for patterns that indicate malicious encryption. It incorporates threat intelligence from VirusTotal and adapts to new ransomware variants.
The intervention: When detected, Drive pauses syncing affected files and creates a “protective bubble” around your cloud storage.
Recovery mechanism: Unlike traditional solutions that require complex re-imaging or expensive third-party tools, Drive’s web interface lets you restore files with standard version history features.
Performance impact: Google hasn’t detailed the computational overhead, but the detection runs locally in Drive for desktop.
Rollout and availability#
Status: Open beta starting now Coverage: Included in most Workspace commercial plans at no additional cost Consumer users: Get the file restoration capability for free Default state: Enabled automatically, but admins can disable it if needed Platforms: Drive for desktop on Windows and macOS
Admin controls: Enterprise administrators can manage detection and restoration capabilities through the Admin console.
What this signals about Google’s strategy#
Beyond productivity: Google is positioning Workspace as an enterprise security platform, not just a collaboration suite.
AI-first security: This represents Google’s approach to using AI for proactive threat detection rather than reactive scanning.
Integration advantage: By building security into Drive itself, Google can respond faster than external security tools that monitor file systems.
Enterprise focus: The automatic inclusion in commercial plans shows Google is targeting business customers who face the biggest ransomware risks.
The broader context#
Ransomware economics: Mandiant reports that ransomware represented 21% of all intrusions last year, with average incident costs exceeding $5M.
Industry impact: Healthcare, retail, education, manufacturing, and government sectors are particularly vulnerable to operational disruption.
Traditional limits: Antivirus solutions haven’t kept pace with ransomware evolution. New approaches are needed.
Google’s positioning: “Ransomware is no longer just an IT issue” but a core business operations problem requiring new defensive strategies.
What’s impressive about this approach#
Behavioral detection: Instead of trying to identify specific malware signatures, Google is detecting the behavior that makes ransomware effective.
Speed of response: Automatic intervention happens faster than human response times, potentially stopping attacks within minutes rather than hours.
User experience: The restoration process is designed for end users, not IT specialists. No complex recovery procedures or specialized tools required.
Continuous learning: The AI model adapts to new ransomware variants automatically, improving detection over time.
The limitations#
Scope: Only protects files that sync through Drive for desktop. Local-only files or other cloud services aren’t covered.
Timing: Detection happens after ransomware is already running and starting to encrypt files. Some damage may occur before intervention.
False positives: Legitimate mass file operations (like batch processing) could potentially trigger alerts.
Platform dependency: Requires Drive for desktop, which not all organizations use for file management.
What comes next#
Expansion: Expect Google to extend this approach to other Workspace services and file types.
Integration: Deeper connections with Google’s broader security ecosystem, including Chronicle and other enterprise security tools.
Intelligence sharing: The threat intelligence gathered could improve detection across Google’s entire security platform.
Industry response: Other cloud storage providers will likely develop similar behavioral detection capabilities.
My take on the timing#
This launch feels like Google responding to the reality that traditional cybersecurity isn’t keeping up with ransomware evolution.
The enterprise opportunity: Businesses are desperate for better ransomware protection. By building it into Drive, Google makes security a competitive advantage for Workspace.
The AI angle: This is a practical application of AI that solves a real problem, not just a feature for marketing purposes.
The integration story: Google’s advantage is that they control the entire stack from file storage to AI detection. That enables faster response times than third-party solutions.
But the real test: How well does this work in practice? False positives could be disruptive, and sophisticated ransomware might find ways to evade behavioral detection.
The bigger questions#
What about other attack vectors? Ransomware often spreads through email, network shares, and other paths. Drive protection is just one layer.
How sophisticated will evasion become? As behavioral detection improves, will ransomware adapt to encrypt files more slowly or selectively?
What’s the performance impact? Continuous AI monitoring of file changes could affect system performance, especially on older hardware.
Who benefits most? Small businesses without dedicated IT security teams, or enterprises with existing security infrastructure?
For IT teams#
Immediate value: This provides protection for a common attack vector without additional software deployment or management overhead.
Complementary defense: Works alongside existing antivirus and endpoint protection, not as a replacement.
User empowerment: End users can restore their own files without IT intervention, reducing help desk burden during incidents.
Visibility: Admin console integration provides the monitoring and audit capabilities IT teams need.
The bottom line: Google is betting that the future of ransomware defense is behavioral detection integrated into the platforms where work happens, not standalone security tools monitoring from the outside.
This approach makes sense. Ransomware has to modify files to be effective. If you can detect and stop that modification quickly enough, you neutralize the attack regardless of how it got in.
Learn more: Read Google’s full announcement and download Drive for desktop to enable the protection.